 |
Stochastic Finite Elements in Hydroelasticity
| Project team leader | Dr.rer.nat. Ralf-Peter Mundani Dipl.-Ing. Stefan Kollmannsberger MSc |
| PhD students | Dipl.-Ing. Iason Papaioannou MSc |
| Principal investigators | Prof. Dr. Hans-Joachim Bungartz (TUM) PD Dr.- Ing. Alexander Düster (TUHH) Dr.-Ing. Holger Heidkamp (SOFiSTiK AG) Dr.rer.nat. Ralf-Peter Mundani Prof. Dr. rer.nat. Ernst Rank (TUM) Prof. Chien Ming Wang (NUS) |
| Project partners | SOFiSTiK AG NUS (National University of Singapore) |
| Sponsorship | SOFiSTiK AG IGSSE (International Graduate School of Science and Engineering) |
| Homepage of the IGSSE-research project |
Hydroelastic analysis of floating structures |
Project description
There is a growing trend in the development of concepts which increase the design quality of structural systems by considering the stochastic nature of input parameters. In this context, a number of methods have been developed that quantify the effect of parameter uncertainties on the structural response. In particular, probabilistic algorithms are coupled with structural finite element solvers to compute the probability of successful performance, i.e. the probability of satisfaction of the design criteria throughout the lifetime of the structure. The corresponding complementary probability is called probability of failure.
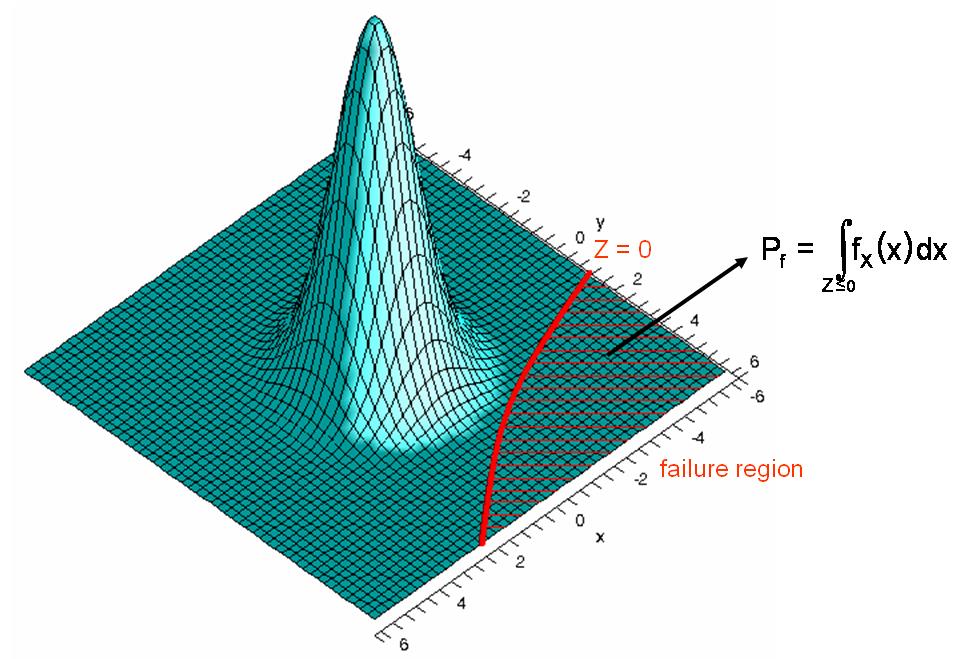
In order to perform the reliability analysis of a structure, the failure criterion is expressed using a performance function, defined with respect to a number of structural components which are subject to an uncertain behavior (e.g. uncertainties in loading, material properties). The zero-isosurface of the performance function is called limit state function and divides the space of the random structural components (also called random variables) to a safe and a failure region. The probability of failure is then computed by integrating the joint probability density function of the random variables, on the failure region.
|
Computation of the probability of failure in a problem with two random variables
|
In this project, a number of reliability methods are investigated with focus on the improvement of accuracy and efficiency, aiming at the application to large-scale industrial problems. The methods considered include approximation and simulation approaches. Approximation methods take the probabilistic nature of input parameters into account but include approximations which limit their application to specific problems. On the other hand, simulation methods are considered to be fully probabilistic methods in the sense that no simplifying assumptions are applied. The methods are optimized, by increasing their robustness and keeping the computational cost to low levels, in order to enhance the applicability to a wide range of problems. The methods are coupled with the SOFiSTiK finite element solver with intent of performing the reliability assessment of real-world industrial problems. A specific domain of application considered is the hydroelastic analysis of very large floating structures in conjuction with the corresponding project, funded by the IGSSE.
Publications
- I. Papaioannou, H. Heidkamp, A. Düster, S. Kollmannsberger, E. Rank, C. Katz:
The subset simulation applied to the reliability analysis of a nonlinear geotechnical finite element model
In: Proc. of the 7th International Probabilistic Workshop. Delft, The Netherlands, 2009.
- Papaioannou, I.; Heidkamp, H.; Duester, A.; Rank, E.; Katz, C.:
Integration of reliability methods into a commercial finite element software package.
In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Structural Safety and Reliability, Osaka, Japan 2009
- Papaioannou, I.; Heidkamp, H.; Duester, A.; Rank, E.; Katz, C.:
Random field reliability analysis as a means for risk assessment in tunnelling.
In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computational Methods in Tunnelling, Bochum, Germany 2009 - Papaioannou, I.; Heidkamp, H.; Duester, A.; Rank, E.; Katz, C.:
Towards efficient reliability methods with applications to industrial problems.
In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, Athens, Greece 2008